Diabetes Insipidus Gfr
Diabetesinsipidus Nhs
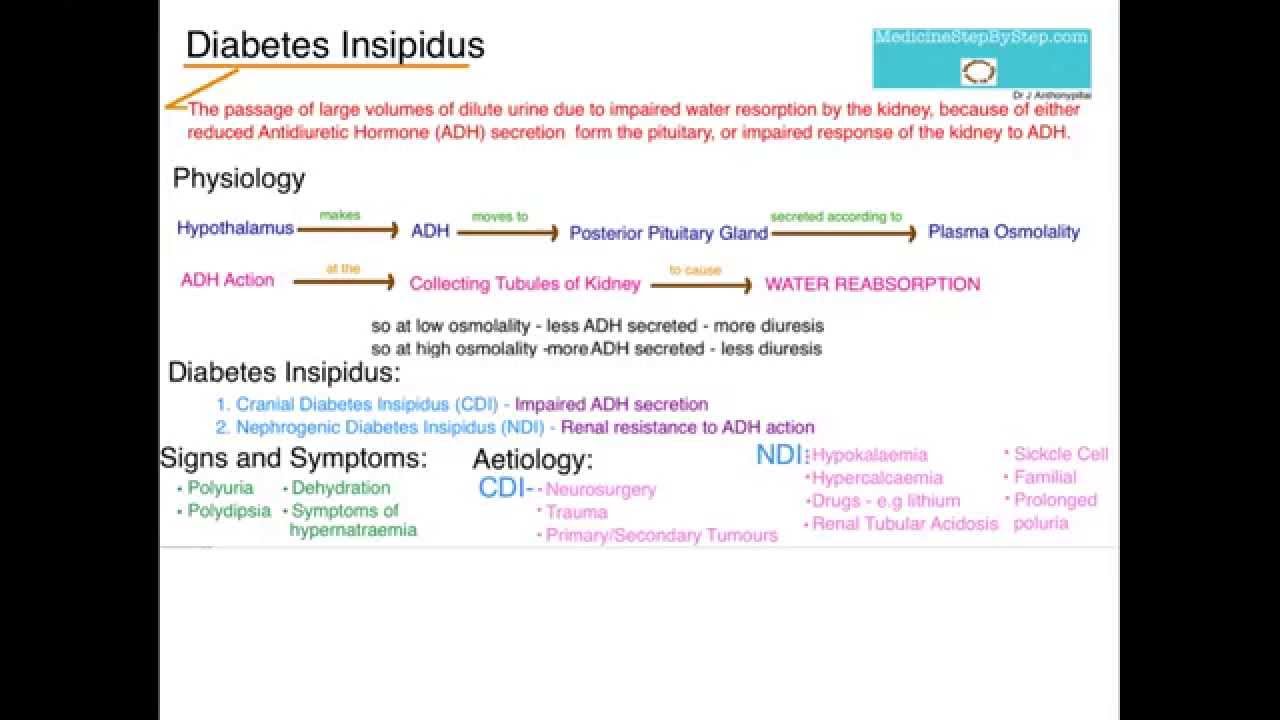
What is diabetes insipidus? diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that causes your body to make a lot of urine that is "insipid," or colorless and odorless. most people pee out 1 to 2 quarts a. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is defined as an uncontrolled solute-free water diuresis (which is also called “aquaresis”) due to an inability to maximally concentrate the urine. most patients with di have modest dehydration, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and have urine volumes in the range of 6-12 liters/day. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. this is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of antidiuretic hormone (adh, also called vasopressin). nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to adh, leading to a decrease in the ability of. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. this is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of antidiuretic hormone (adh, also called vasopressin).
Congenital Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus In A Preterm
Introduction. diabetes insipidus (di) is the failure of the renal tubules to conserve water. if not corrected, this can lead to symptoms of polydipsia and dilute polyuria, and can result in hypernatraemic dehydration with neurological sequelae such as weakness, confusion and seizures. 1 it is a rare complication of pregnancy occurring in approximately 2–4 per 100 000 pregnant women. 2, 3. Diabetesinsipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of diabetes insipidus gfr urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day.
They may reduce urine volume, but generally by no more than 10 to 25%, perhaps by decreasing renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (gfr). together with indomethacin, restriction of sodium intake and a thiazide diuretic help further reduce urine volume in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus (di) is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. di is not the same as diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. however, untreated, both di and diabetes mellitus cause constant thirst and frequent urination. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is diabetes insipidus gfr an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. di is not the same as diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. however, untreated, both di and diabetes mellitus cause constant thirst and frequent urination. people with diabetes mellitus have high blood sugar (glucose) because the body.
Diabetes Insipidus Niddk
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is an inability to concentrate urine due to impaired renal tubule response to vasopressin (adh), which leads to excretion of large amounts of dilute urine. it can be inherited or occur secondary to conditions that impair renal concentrating ability. Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day. Diabetes is recognised as a major risk factor for the development of ckd. in developed countries, diabetes diabetes insipidus gfr is the leading cause of esrd and diabetic subjects with ckd are at high risk for developing cvd. gfr is usually accepted as the best overall estimate of kidney function and therefore is commonly used to evaluate onset and progression of ckd.
More diabetes insipidus gfr images. The diagnosis of diabetes insipidus (di) is often made clinically, while the laboratory tests provide confirmation. perform testing with the patient maximally dehydrated as tolerated, that is, at a time when adh release would be highest and urine would be most concentrated.
Central Diabetes Insipidus Endocrine And Metabolic
Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.. there are four types of di, each with a different set of causes. Diabetesinsipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related. Introduction. hypokalemia, especially if persistent, can induce a variety of changes in renal function, impairing tubular transport and possibly inducing chronic tubulointerstitial disease and cyst formation []. one function that is not impaired is the ability to appropriately conserve potassium, which can be important in distinguishing between extrarenal and renal sources of potassium loss.
The most common problem from taking lithium is a form of diabetes due to kidney damage called nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. this type of diabetes is different than diabetes mellitus caused by high blood sugar. in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, the kidneys cannot respond to anti-diuretic hormone (adh), a chemical messenger that controls fluid. Diabetesinsipidus is not related to diabetes, but it does share some of the same signs and symptoms. the 2 main symptoms of diabetes insipidus are: extreme thirst (polydipsia) peeing a lot, even at night (polyuria) in very severe cases of diabetes insipidus, a person can pee up to 20 litres of urine in a day. The authors have evaluated urinary adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic amp) excretion and renal function during pitressin administration, hypertonic saline administration, and water deprivation in two siblings with vasopressin-resistant diabetes insipidus and in normal control subjects.
Uptodate
In patients with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, urine output may reach up to 15 liters per day. if fluid intake does not match output, people may become so dehydrated that they develop neurological symptoms such as fatigue, headache, or lethargy. a standard measure of overall kidney function is the glomerular filtration rate (gfr). one. Which of the following conditions could cause diabetes insipidus? pituitary tumor. the minimum urine volume needed to excrete metabolic wastes produced by the body is called as. (glomerular filtration rate); conversely, when the secretion of a substance increases, its renal plasma rate is _____ the gfr. Renal azotemia refers to a reduction in glomerular filtration rate (gfr) of ~75% during acute or chronic primary renal diabetes insipidus gfr (or intrarenal) diseases. diabetes mellitus), central diabetes insipidus, and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (eg, hyperadrenocorticism, hypercalcemia, pyometra, diseases causing septicemia). adrenal insufficiency leads to a. Diabetes insipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related.
Diabetes insipidus niddk.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a disorder of water balance. the body normally balances fluid intake with the excretion of fluid in urine. however, people with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus produce too much urine (polyuria), which causes them to be excessively thirsty (polydipsia). affected individuals can quickly become dehydrated if they do not drink enough water, especially in hot. Diabetesinsipidus occurs when either the secretion or action of antidiuretic hormone (adh) goes awry. produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary, adh causes fluid retention or lack of diuresis. in large amounts, adh—also known as vasopressin—constricts arterioles. diuretics may decrease the glomerular filtration. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. [1] reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. [1].
Lithium-induced kidney problems harvard health.
Congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (ndi) is a rare condition that associates polyuria and polydipsia as a result of the inability to concentrate urine despite normal or increased levels of antidiuretic hormone (adh). (1. 32 mg/dl) and decreased glomerular filtration rate (gfr, 11. 3 ml/min/1. 73 m 2), while psp values increased to 1647. By conserving water, adh helps increase blood volume and blood pressure (bp) and return serum osmolality to normal. diabetes insipidus ensues when the hypothalamus doesn't produce enough adh, the posterior pituitary doesn't release adh, or the nephron can't act in response to adh. diabetes insipidus occurs in two forms. Diabetesinsipidus results from a deficiency of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone [adh]) due to a hypothalamic-pituitary disorder (central diabetes insipidus) or from resistance of the kidneys to vasopressin (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus). polyuria and polydipsia develop. diagnosis is by water deprivation test showing failure to maximally concentrate urine; vasopressin levels and response to.

Comments
Post a Comment