Diabetes Mellitus Vascular Complications
Introduction. the number of people with diabetes mellitus is alarmingly increasing due to the growing prevalence of obesity, genetic susceptibility, urbanization, and ageing. 1,2 type 2 diabetes, the most common form of the disease, may remain undetected for many years and its diagnosis is often made incidentally through an abnormal blood or urine glucose test. View this table: vascular complications of diabetes view this table: risk of morbidity associated with all types of diabetes mellitus a continuous relation exists between glycaemic control and the incidence and progression of microvascular complications. hypertension and smoking also have an adverse effect on microvascular outcomes. (july 2017) (learn how and when to remove this template message) complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability.
Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). Young people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (t1dm) are at risk of vascular complications. in this perspectives article, m. loredana marcovecchio and colleagues present a new framework for managing.
Vascular complications of diabetes circulation research.
Six Diabetesrelated Vascular Complications And How To
Six diabetes-related vascular complications and how to.
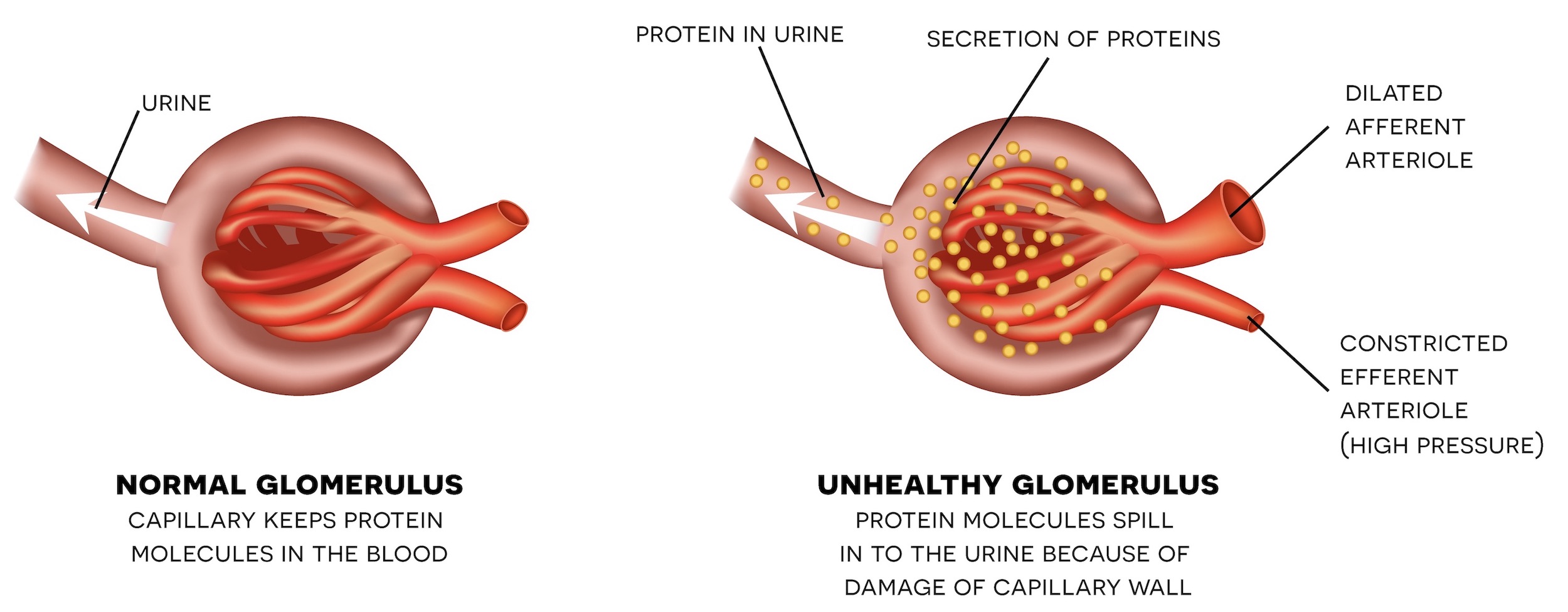
Diabetesmellitus affects approximately 100 million persons worldwide. 1 five to ten percent have type 1 (formerly known as insulin-dependent) and 90% to 95% have type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. it is likely that the incidence of type 2 diabetes will rise as a consequence of lifestyle patterns contributing to obesity. 2 cardiovascular physicians are encountering many of. Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a important health problem that induces ernestful complications and it causes significant morbidity owing to specific microvascular complications such as, retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy, and macrovascular complications such as, ischaemic heart disease, and peripheral vasculopathy. Diabetic retinopathy may be the most common microvascular complication of diabetes. it is responsible for ∼ 10,000 new cases of blindness every year in the united states alone. 1 the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy or other microvascular complications of diabetes depends on both the duration and the severity of hyperglycemia.
Diabetesmellitus may increase the risk of venous thromboembolism (vte) via its effect on platelets and the components of the coagulation cascade. 172 174 in a retrospective study of >700 000 veterans affairs patients, using international classification of diseases-9 codes to identify diabetes mellitus, the risk of pulmonary embolism was 27. Patients with diabetes mellitus have other conditions that contribute to foot wounds and exacerbate the complications of vascular insufficiency, such as neuropathy and altered foot mechanics. the presence of these additional complications may make determination of the pathogenesis of pedal ulcers more difficult to ascertain. The management of type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus (dm) requires addressing multiple goals, with the primary goal being glycemic control. maintaining glycemic control in patients with diabetes prevents many of the microvascular and macrovascular complications associated with diabetes.
Diabetes And Vascular Disease Circulation

Japanese migrants and their offspring on the island of hawaii and japanese living in hiroshima were examined for diabetes mellitus and its vascular complications. the same methods and investigators were used in both locations. death certificates of japanese and caucasians dying on the island during the past 26 yr were analyzed. diabetes, defined as a venous serum glucose concentration of at. The effects of glycemic control on microvascular and macrovascular complications in type 1 diabetes will be reviewed here. glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes is discussed separately. (see "glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus". ) pathogenesis. You are currently caring for a patient with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. what long-term complications may be of concern? which of the following conditions is not a long-term complication associated with diabetes mellitus? joint and muscle pain. coronary artery disease cardiovascular disease peripheral vascular disease blindness. joint. The most well-established clinical advances in preventing vascular complications of diabetes include intensive blood glucose lowering which decreases the risk of nephropathy and retinopathy, antihypertensive medicine which decreases the risk of cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, and retinopathy, panretinal photocoagulation and agents targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf) which slows the progression of diabetic retinopathy, and statin therapy which reduces the risk of.
See more videos for diabetes mellitus vascular complications. Background. type 2 diabetes is associated with disabling and potentially life-threatening microvascular and macrovascular complications [1, 2]. as many as 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes develop cardiovascular complications, which account for approximately 65% of deaths in this group [3–5]. the contribution of microvascular complications to type 2 diabetes morbidity is also substantial [2. In patients with diabetes mellitus (dm), years of poorly controlled hyperglycemia lead to multiple, primarily vascular, complications that affect small vessels (microvascular), large vessels (macrovascular), or both. In conjunction with national diabetes awareness month in november, here is how six vascular complications are aggravated by diabetes: diabetic eye disease. diabetes' effect on the vascular system is what causes diabetic eye disease. the tiny blood vessels in the retina become swollen, which blocks the oxygen supply to the retina.
Longterm Complications Of Diabetes Flashcards Quizlet
The association between hyperglycemia and inflammation and vascular complications in diabetes is now well established. antidiabetes drugs may alleviate inflammation by reducing hyperglycemia; diabetes mellitus vascular complications however, the anti-inflammatory effects of these medications are inconsistent and it is unknown whether their beneficial metabolic effects are mediated via modulation of chronic inflammation. Diabetes is a group of chronic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia. modern medical care uses a vast array of lifestyle and pharmaceutical interventions aimed at preventing and controlling hyperglycemia. in addition to ensuring the adequate delivery of glucose to the tissues of the body, treatment of diabetes attempts to decrease the likelihood that the tissues of the body are harmed by. Complications of diabetesmellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels.

But some may not understand that many of the most common complications of diabetes mellitus vascular complications diabetes stem from one primary issue: the havoc that high blood sugar, also called hyperglycemia, causes for the body's blood vessels. because blood brings oxygen to every living cell in the body, when blood vessels aren't working properly, the body suffers. Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance are key players in the development of atherosclerosis and its complications. a large body of evidence suggest that metabolic abnormalities cause overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ros).
The vascular complications of diabetes are classified as either microvascular (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) or macrovascular, which includes coronary artery, peripheral, and cerebral vascular disease. the microvascular complications can develop within 5 years of the onset of t1d, but infrequently develop before the onset of puberty. Introduction. the vascular complications of diabetes are the most serious manifestations of the disease. atherosclerosis is the main reason for impaired life expectancy in patients with diabetes whereas diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are the largest contributors to end-stage renal disease and blindness, respectively.
In people with diabetes macrovascular complications are two times greater than microvascular complications 20% 9% 0 5 10 15 20 25 macrovascular complications microvascular complications. Glycemic targets and the effects of glycemic control on microvascular and macrovascular complications diabetes mellitus vascular complications in type 2 diabetes will be reviewed here. glycemic control and vascular complications in type 1 diabetes, the mechanism by which hyperglycemia might cause these complications, and an overview of the treatment of diabetes are discussed separately.
Comments
Post a Comment